Exploring Digital Business Life Cycle
3AI November 6, 2020

As per Gartner, Digital business could be defined as “the creation of new business designs by blurring the digital and physical worlds”. The adoption of Digital Business, which is a precursor to Business Analytics, is not a new phenomenon relatively, as companies have been adopting a simpler and more rudimentary version of the Digital Business that we know today. Today we are going to describe in detail, the various stages of Digital Business adoption. This could be used by the Executives and CXOs of companies to assess their standing in the Digital Conversion of their business and find out how much ground is left to cover.
Most of the companies have been calling themselves Digital, but most have yet to transcend to being purely digital businesses but are instead left to being an e-business or a digital marketing business. 41% of businesses have their primary focus on digital marketing. This state of illusion could lead to competitors seriously hurting them.
What Is Required To Become A Digital Business?
Digital Business primarily brings a convergence of people, business and things, which attains ability to disrupts existing business models. The perception of an Innovative business painted by Digital has been defined as the interaction of people, business and things. The disruptive business would the one which can successfully come up with an efficient way for these three entities to interact with each other to create value. The following figure depicts the individual rendition of various companies of how they define being part of Digital.
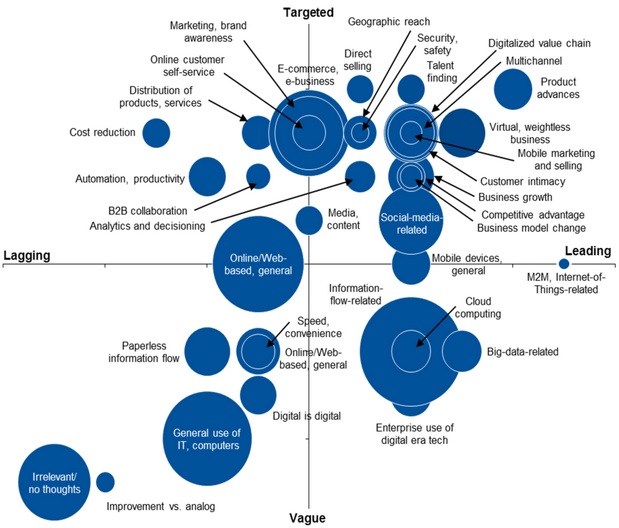
Digital Business Model Perspectives
The CIOs can now see that, for example, even if they are a very successful e-business, their model is susceptible of becoming irrelevant in the near future because of a new entrant leveraging Digital Business Capabilities. For many industries, the competitive landscape is turbulent, with new entrants pouring in constantly, while making the incumbents to review their business model.
Six Stages of Digital Business Life Cycle
The Digital Business Life Cycle can be perceive to contain six stages of digital evolution. The characteristics of the same is described in the figure below:
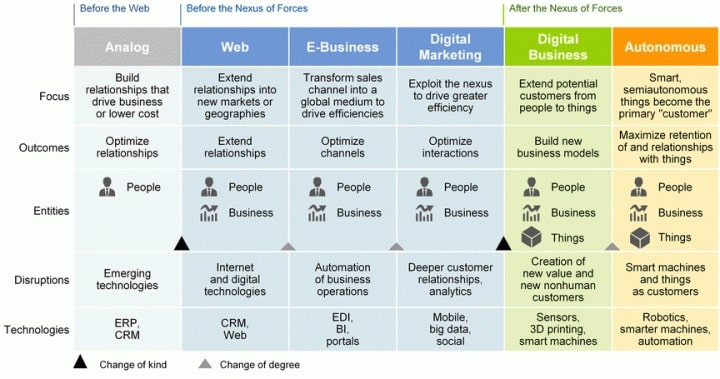
Digital Business Models
This figure will help CIOs make the case for digital business investments. The characteristics are divided into five attributes:
- Focus —The business focus of a particular model, which is also the objective of the Digital Business Model. This could be on improving the internal productivity which lowers the costs, or to make foray into new markets, finding new source of revenue, or getting new customers.
- Outcomes —This contains the outcomes from a particular model, the cause of which are the aspects of Focus defined above.
- Entities —This contains the entities that play the role of actors in the business, whose interplay leads to creation of value and subsequently a scalable and profitable business. For analog business, people served as a proxy for things and even businesses. For digital business and beyond, the three entities of people, business and things, integrated together, after the Nexus of Forces, leads to creation of value. The distinction and interaction between the three is only to become more pronounced with the advent of mainstream adoption of Internet of Things and Autonomous Systems.
- Disruptions —This describes the factors – which could be technology, entities or ideologies which leads to disruption in businesses.
- Technologies —This identifies the various technologies tools, methodologies and trends that enable a particular business model in a certain stage. This would indicate the technological trends which would be forayed from hype generation into mass adoption.
Let’s look at the various stages in a bit more detail:
Analog Business
This stage of development was at the height of business before Internet came into being. The primary targets were to improving revenue or reducing costs. Internet only acted as a medium of communication between suppliers, customers and businesses. Technologies like mobile, social or e-commerce where the business disrupters of these times.
Web Business
In this stage, the business had a good presence on the Internet which was mostly used for basic level promotions of making people familiar with the name and its workings. The attributes of this level of business are:
- The business is engaged in making its presence known to increase its business volumes by increasing personal traffic, phone calls or email.
- This does not require a lot of communications to be managed. It may be a government license to operate that grants an effective monopoly for political purposes.
- Security wise they used to consider Internet too risky as technology for secure transactions were not in place yet.
- This businesses were mostly in parts of the world where Internet infrastructure had not yet flourished to the state of reliability to operate.
E-Business
In this stage, the goals of the analog business achieve scalable performance when combined with the reach of the Internet. For many businesses, e-business led to a great success. For others, they would sustain until a business armed with digital business strategies invades their space. The key to e-business is not only to focus on business relationship, but also business integration. It uses internet to leverage its reach across to the mass, something which business had trouble of achieving. An e-business exploits the reach, availability and ubiquity of the Internet and was able to connect customers and businesses together.
Digital Marketing
Consumers have declared their mobile devices and social networks as preferred doorways to companies. By the advent of Digital Business, there was a clear increase in the priority businesses gave to customer expectations. Customers exercise a huge influence on brands, markets, products and even pricing. The biggest challenge for the CMOs is to leverage the ever-changing customer expectations to grow the company. Digital marketing transforms the relationship a company has with its customers, building on a preferred technology platform. The adoption of Digital Marketing has led to a more closer connect with the customers, their needs, preferences and aspirations. This also follows the increase in the influencing power of customers due to availability of many players and the power to choose a vendor or to migrate to another.
Digital Business
Digital business promises to bring in an unprecedented convergence of people, business and things which has the potential, and which does to this day, disrupt existing business models — even those born in the era of Internet and e-business.
Some of the attributes of digital business are:
- Things become agents for themselves, for people and for businesses. The increase in interconnectivity, communication and exchange of intelligence of things makes many of them, not only agents for providing services but also the frontiers of making business decisions.
- Nearly all physical and virtual assets in the value chain are in a digitized form. The spectrum of intelligent things interact and work together to incorporate an end-to-end process.
Digital business represents another big change in trend, with the entry of Internet of Things, which creates a completely different interworking.
Autonomous Systems
The final frontier for the Digital Business, subsequent to continuous improvement in the intelligence of things would be a Business where primary entities work, interact, negotiate and decide with zero human intervention. This has the potential to influence deeply, the lives of people, and the quality of life itself. Technologies like Autonomous vehicles are already into prototype stage which, when perfected, would lead to a breakthrough in industries and practices like transportation, mining and defense. In addition to the self-managing aspects of these things, there will be an immense improvement in the quality of output due to real-time interaction and decisive performance by these Autonomous Systems. They would further open doors to advanced Artificial Intelligence systems which could self-heal and evolve independently.
This Life Cycle is designed to help companies have a precise understanding of their current stage of digital business transformation, and then to identify the way forward with the support of top level management and board of directors, given the complexities of integrating with the world of digital business.






