Cryptography and the Analytics Interventions: few Perspectives
3AI November 24, 2020

The long-standing desire for two parties to transact online directly—without a third-party intermediary— has accelerated the popularity of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Litecoin, Blackcoin, Dogecoin etc. The online equivalent of hand-to-hand cash transactions, the cryptocurrency phenomenon, which is driven primarily by its to-date most popular option, Bitcoin, has struck a chord with growing legions of speculators, consumers, merchants, government regulators and even lawbreakers. As the news of recent Bitcoin-centric scandals has revealed, the latter category of less ethical players has rightfully heightened stakeholder scrutiny and wariness of Bitcoin and its digital brethren. But its growing popularity as a legitimate currency exchange option means Bitcoin holds opportunities as well as risk. Companies are seeking to further capitalize on the Bitcoin trend—even if many remain unsure of the precise implications on their business or industry.
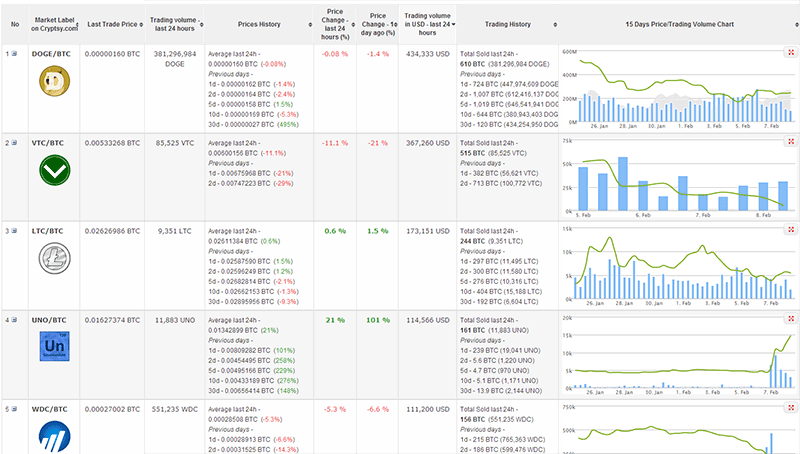
Assessing Bitcoin value with Analytics
Traditional financial industry players—from banks to credit card payment processors—are also sensing that Bitcoin is a disruptive technology that may inalterably change their world order. So, too, are retailers and other product/ service providers who are trying to determine if Bitcoin is a payment option they should embrace on behalf of consumers seeking cryptocurrency benefits. These benefits can extend beyond the notion of currency. From every Bitcoin transaction, valuable data emerges. While anonymity is a hallmark of cryptocurrencies, every transaction is at its basic element a contract, with conditions and limitations, and anonymous or not, that data has value. From the timing, nature of spending, conditions, and limitations of these contracts between sender and receiver, trends will emerge that have the potential to feed new business models and transform long-standing processes. Analytics solutions can extract and interpret data to provide valuable insights about— and beyond—the transaction. Opportunities for Bitcoin transaction analysis are emerging within the following categories:
Block Chain Ingestion
Because the block chain is a public ledger of all transactions, analytics solutions can access and analyze vast amounts of data residing there. Doing so can unearth valuable information that can reveal specific insights on the audience for Bitcoin payments and transfers. For instance, credit card companies may be interested in delving into Bitcoin transactional data to determine the extent of the technology as a competitive threat. As a result, these companies can more effectively optimize pricing or target marketing campaigns to counter Bitcoin’s actions and consider how the block chain may evolve. Although the block chain is transaction focused, in the future it may be possible to glean more information from it; this could be a move beyond historical and chronological information, and reflect more complex relationships among participants.
Transaction Tracing
Many Bitcoin owners and exchanges have inquired about getting private insurance for their often sizeable Bitcoin portfolios. Should insurance companies offer it? And at what price? What business models might emerge around insuring such cryptocurrencies? If insurers have the capability of proving whether or not Bitcoin transactions have been stolen via the loss or theft of account keys, they can adjudicate claims more accurately and expeditiously.
Identity Resolution
Naturally, the anonymity of the sellers and buyers using Bitcoin can lead to nefarious activity, including money laundering and other illegal transactions. Since the transactions are publicly documented, a number of Web scraping tools can be used by law enforcement officials or other entities seeking either to unmask Bitcoin users or statistically verify trends related to transactions.
To date, at least two academic research efforts have been conducted to not only derive the identities of users but to determine transaction usage and circulation patterns. Each involved downloading the full history of the Bitcoin scheme into a transaction graph, and then thoroughly analyzing it. This research revealed that transactions involving a large number of Bitcoins involved creating chains of smaller, consecutive transactions that used forkmerge patterns and self-loops in an obvious attempt to conceal their ultimate destinations. Additionally, persistent “detectives” can often ascertain more specific information—even Bitcoin wallet addresses—by using analytics tools to mine online message boards and other social media sites where Bitcoin topics are discussed. One caveat—conclusions reached are highly subjective or directional in nature, since specific information remains extremely difficult to ascertain.
Finally, financial institutions with customers who hold assets in Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies can and would need to use analytics tools and techniques to ensure compliance with Bank Secrecy Act and other anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. Particularly, the publicly available nature of the block chain makes it both possible and necessary to use these techniques to perform deep transaction reviews of customers, although somewhat contradictorily, the pseudonymity in the block chain addresses makes it difficult to ascertain transactional counterparties.
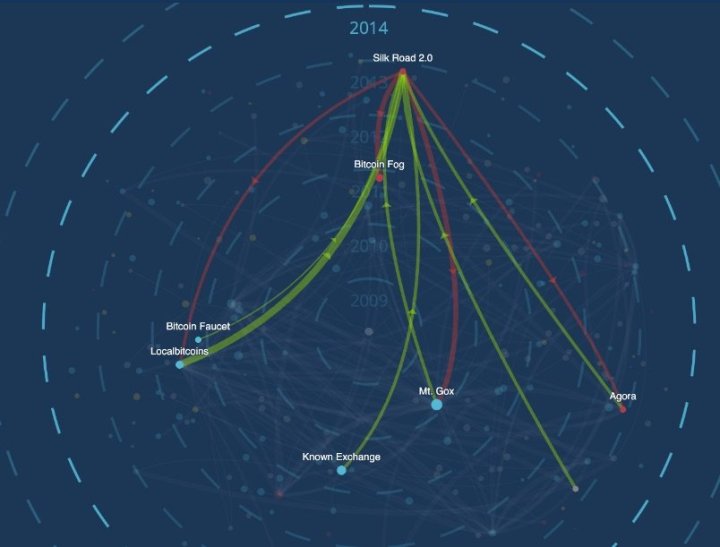
International Transfers
Bitcoin has a number of international political implications, as the relative anonymity of cryptocurrency transfers can enable rogue states or nations facing sanctions to circumvent those deterrents. Thus, a number of national and global governing bodies have become interested in tracking Bitcoin and other transactions that facilitate money movement outside of mainstream networks. On a more positive note, the speed of Bitcoin transactions can make it an appealing option for legitimate international transactions that would otherwise face considerable delays while the parties navigate the tricky (yet perhaps more secure) conventional monetary exchange platforms.
Predictive Capabilities
While the Bitcoin analyses conducted to date have revealed an often labyrinthine pathway of transactions, business and government entities are heartened by the promise of advanced data analytics tools in predicting future transactions or patterns. This area is likely to expand if Bitcoin’s growth and popularity continue and it becomes more of a mainstream monetary exchange, with much of the predictive work likely to involve Bitcoincentric dialogue that is occurring more frequently via social networks. Since Bitcoins can be viewed as assets, then as with other asset classes, it may be possible to use transaction volumes and history to attempt to predict value and securitize portfolios of Bitcoins.
Positioning For Disruption
Throughout history, direct hand-to-hand exchange of currency has been the most popular method of transacting business. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are the digital equivalent of these currency exchanges, and come with a phalanx of advantages, challenges, and still-unknown implications that seem likely to entice or frighten numerous stakeholders. Traditional remittance and money transfer businesses may be at risk of significant market disruption if cryptocurrencies continue to grow in popularity. Services conducting money transfers through Bitcoin can adjust their pricing and marketing to benefit from Bitcoin’s advantages vis-à-vis traditional money transfer services. Moreover, new remittance solutions based on cryptocurrencies are possible and can be focused on major markets. Financial institutions can identify those merchants willing to accept Bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies and potentially market customized financial services and products around cryptocurrencies to these merchants. Cryptocurrencies are not limited to transactions as simply monetary instruments; their positioning as assets may allow them to be used in larger swap or derivative transactions as an underlying asset. Businesses that implement analytical processes and technologies now may be better positioned to mine the real gold from cryptocurrencies over the long term.