Preparing to navigate the era of AI regulation
3AI September 10, 2024

Featured Article
Author: Malavika Lakireddy
In a groundbreaking move, the European Union (EU) has recently passed the Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act), signaling a pivotal moment in the global landscape of AI regulation. This legislation, aimed at regulating the use of AI in providing goods and services to EU residents, sets a precedent for similar initiatives worldwide. As the adoption of AI technologies becomes increasingly prevalent and influential, jurisdictions including the US, India, China, Australia, the Middle East, and beyond are contemplating their own regulatory frameworks.
While the AI Act currently pertains specifically to EU residents, its principles are poised to become foundational for AI legislation in other regions. This mandates that global companies proactively prepare for compliance with these evolving laws within their organizations, processes and product offerings.
An Overview of the EU AI Act
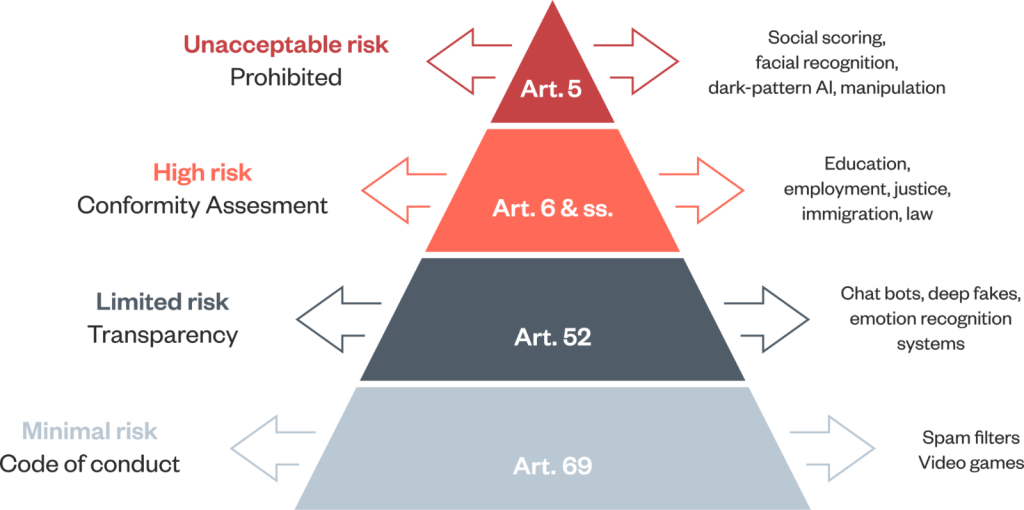
The EU AI Act delineates a comprehensive framework for developers and deployers, outlining clear requirements and obligations concerning specific uses of AI. Employing a risk-based approach, the legislation categorizes AI applications into different risk levels:
- Unacceptable Risk Use Cases: These encompass scenarios such as subliminal manipulation, biometric categorization, predictive policing, and exploiting system vulnerabilities. The Act prohibits the use of AI in such cases to safeguard against bias and critical risks to consumers.
- High-Risk Use Cases: These include AI applications deployed in critical infrastructure, healthcare, education, and public services like credit scoring and judicial procedures. High-risk AI systems must adhere to stringent obligations before deployment, including risk assessment, data quality assurance, transparency, human oversight, and security measures.
- Limited Risk and Minimal to No-Risk Use Cases: These categories cover less sensitive applications where transparency to end consumers regarding AI usage is encouraged, but fewer regulatory constraints apply.
https://www.adalovelaceinstitute.org/resource/eu-ai-act-explainer
Preparing Your Organization
To navigate the complexities of AI regulation effectively, organizations must undertake proactive measures:
- Establish an AI Governance Body: Consisting of representatives from Legal, Product, Engineering, and Business teams to ensure comprehensive oversight and accountability.
- Define AI Use Policies and Governance Frameworks: Articulate acceptable AI use cases and establish frameworks for data protection, privacy, explainability, bias mitigation, and risk assessment across all organizational functions.
- Implement Monitoring Processes: Develop protocols for monitoring AI usage throughout the organization and regularly assess compliance with regulatory requirements.
Preparing Your Team
Equip your team with the necessary awareness and skills to ensure AI compliance:
- Educate on AI Laws and Compliance: Foster awareness among employees across all teams about AI laws and regulations, emphasizing the qualification of use cases by risk levels. For e.g. using ChatGPT may be acceptable for marketing content but not for contracts and patent filing.
- Integrate Compliance Assessment: Integrate AI Act assessment into project discovery and requirements gathering phases, with ongoing collaboration with legal teams for clarifications.
- Ensure appropriate documentation: The AI use cases with details spanning responsible AI framework need to be documented, which serves both for assessing risks and meets regulatory requirements for reporting.
Preparing Your Product
Ensure that your products adhere to regulatory standards and prioritize user privacy and transparency and addressing bias and ethical use risk.
- Safeguard User Privacy: Ensure appropriate safeguards are put to meet user privacy concerns. This includes updating terms and conditions and Master Service Agreements, ability for users to opt out from using their data for optimization etc.
- Data protection safeguards: Ensure sensitive data protection by obfuscation, adding noise, differential privacy, excluding sensitive and PII data from model training etc,
- Transparency & Compliance: Enable transparency of use of AI through product and feature labeling in UI for AI driven capabilities
- Ensure Data Quality and Model Robustness: Utilize high-quality data for model training, implement fallback mechanisms for seamless user experiences,
- Risk assessment & monitoring: Invest in ML Ops for continuous monitoring and maintenance of AI models including logging outputs and periodically assessing models for bias.
In conclusion, as global companies brace for the era of AI regulation, investing in robust AI governance practices is imperative. By proactively aligning with evolving regulatory landscapes, organizations can not only ensure compliance but also foster trust and transparency in their AI-driven products and services.
Title picture: freepik.com






